
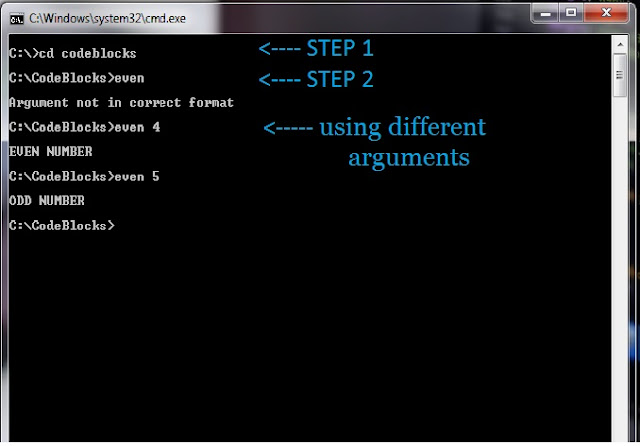
Select the Search Directories tab and then select the Compiler tab.Solarian Programmer My programming ramblings Home Archives Contact Privacy Install Code::Blocks and GCC 9 on Windows - Build C, C++ and Fortran programs Posted on Novemby Paul On my machine the compiled library files were located in the /usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/ folder:Īs with the Windows compiled library example, right-click your project folder and select Build Options. If you are unsure of where your Boost libraries have been installed in Linux, the locate We now configure the include and library paths etc. Std::cout << "main: waiting for thread" << std::endl Std::cout << "main: startup" << std::endl Std::cout << "Worker: finished" << std::endl

Std::cout << "Worker: running" << std::endl Insert the following code in main.cpp which exercises the Boost Threads library: Std::string filename = p.filename().string() % now.date().year_month_day().month.as_number()īoost::filesystem::path targetDir( "C:\\MyStuff" ) īoost::filesystem::directory_iterator it( targetDir ), eod īOOST_FOREACH( boost::filesystem::path const &p, std::make_pair( it, eod ) ) % now.date().year_month_day().day.as_number() Paste the following into the main.cpp file you just created:Ĭonst boost::posix_time::ptime now = boost::posix_time::second_clock::local_time() Ĭonst boost::wformat f = boost::wformat( L"%02d.%02d.%s %02d:%02d" ) Then make sure the Debug and Release checkboxes are set:Īn example that only requires the use of non-compiled libraries, the Boost.DateTime example. Click Yes when prompted if we wish to add this to the current active project: Select File > New > Project > Empty Project:Ĭhoose the C++ compiler you are currently using, such as Cygwin or MinGW and then click Finish:Īdd the main.cpp source file by selecting File > New > Empty File. To configure Code::Blocks to use a header-only Boost library: Boost.DateTime. Some examples of how to configure Code::Blocks to use the Boost C++ libraries:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
